
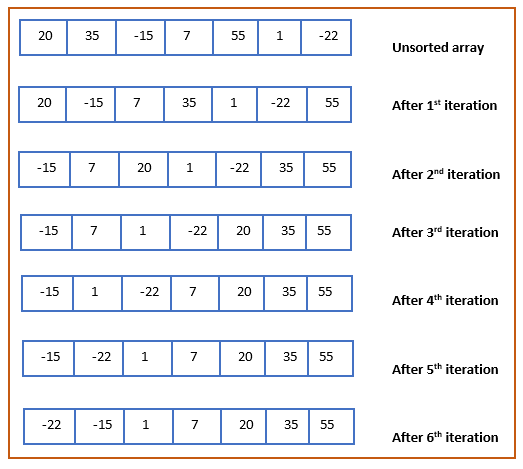
The above illustration can be summarized in tabular form as shown below:Īs shown in the above example, the largest element bubbles up to its proper position with every iteration/pass. Sort An Array Using Bubble sortĪs you can see above, the array is entirely sorted. We take an array of size 5 and illustrate the bubble sort algorithm. Now let’s demonstrate the Bubble Sort Technique using an illustrative example. The general algorithm for Bubble Sort Technique is given below: After comparing if the first element is greater than the second, then the two elements are swapped if they are not in order. If there are n elements in list A given by A,A,A,A,….A, then A is compared to A, A is compared to A and so on. Thus, at the end of the iteration, the heaviest element gets bubbled up to claim its rightful position. This technique sorts the collection by repeatedly comparing two adjacent elements and swapping them if they are not in the desired order. Bubble Sort In Javaīubble sort is the simplest of all sorting techniques in Java. Let’s discuss the Bubble Sort Technique in Java. Uses divide and conquer to sort the collection.įinds the smallest element in the collection and put it in its proper place at the end of every iterationĮlements are sorted by building min heap or max heap.Īpart from the sorting techniques given in the above table, Java also supports the following sorting techniques:īut these techniques are used sparingly in practical applications, thus these techniques will not be part of this series. Most efficient and optimized sorting technique. Divides the collection into simpler sub-collections, sorts them and then merges everything It follows the divide and conquer approach. Inserts each element of the collection in its proper place. At the end of each iteration, the heaviest element gets bubbled up at its proper place. Compares the current element to adjacent elements repeatedly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
